Differential Global Position System (DGPS).
Eliminate potential human errors – accurate tagging of blast holes.
Semi – autonomous tagging method of blast holes.
Easy, reliable and fast deployment to speed up the blasting process.
When blast hole GPS coordinates are not available the DGPS Tagger can log hole positions and import into ViewShot 3D software.
Capable for the integration into future fully autonomous (robotic) deployment and tagging.

“The Most Advanced Electronic Blasting System”
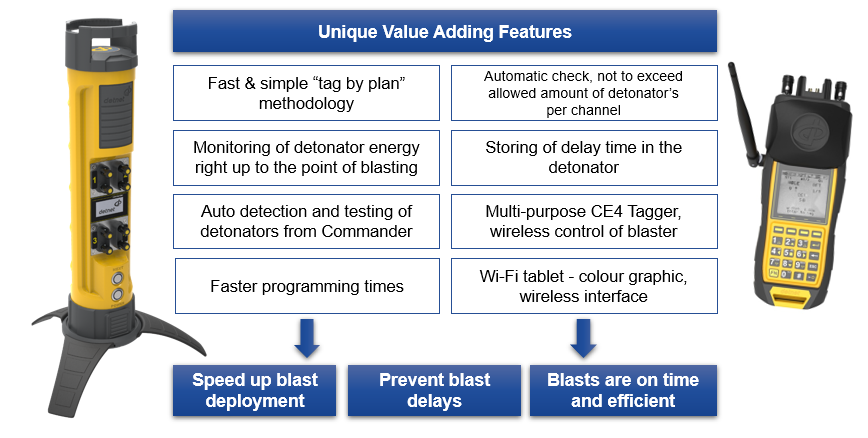
Unique Value Adding Features. Read the DGPS Sales Slick to learn more.
Case Study

Challenges
Customers across the mining industry experience common problems when tagging/logging detonators, these include:
Incorrect delay assignment due to
- Incorrectly marked blast holes
- Incorrect tagging of a hole or delay
- The lack of a blast plan
Blast delays
- Difficulty locating the correct blast hole
- Delays due to time taken to find a problematic hole when fault finding and troubleshooting on the bench
Blast outcomes
- Incorrect timing will impact blast results in fragmentation, loading efficiency, and overall productivity

Opportunity
DGPS can
- Eliminate potential human errors - accurate tagging of blast holes.
- Semi - autonomous tagging method of blast holes.
- Easy, reliable and fast deployment to speed up the blasting process
- When blast hole GPS coordinates are not available the DGPS Tagger can log hole positions and import into ViewShot 3D software.
- Capable for the integration into future fully autonomous (robotic) deployment and tagging
Value to Customers
Speeds up the tagging process and eliminates any possibility of human error.

Feature Overview
Auto Hole Detection
- Eliminates any possibility of human error during the tagging process.
- No blast plan required on bench.
- Flexible tag path. Start at any hole and tag in any sequence.
- No delays due to the loading sequence.
Easy to Use
- Minimal training.
Speeds up the Tagging Process
- Flexible tagging options without any button presses.
GPS Fault Finding
- The tagger will guide the user to the faulty hole.
Engineering/Management Control
- Supply more control as to the design and tagging of the actual hole.

Difference between GPS and DGPS
Normal GPS:
- Provides a position of an object on earth using signals generated by satellites revolving around the earth.
- GPS uses standalone receivers where the location is directly calculated but is also prone to errors such as orbit errors, multi-path errors and clock errors.
- Provides a position of an object on earth using signals generated by satellites revolving around the earth.
- GPS uses standalone receivers where the location is directly calculated but is also prone to errors such as orbit errors, multi-path errors and clock errors.
As a result GPS can gain a nominal accuracy of 10 – 15 meters.
Hence...
GPS is NOT suitable for accurate blast hole position.
Differential GPS:
- Accuracy of DGPS is achieved by using a reference receiver (CE4 Commander) at a known surveyed location that broadcast correction data to the Tagger.
- Accuracy of DGPS is achieved by using a reference receiver (CE4 Commander) at a known surveyed location that broadcast correction data to the Tagger.
- DGPS is a vast improvement from GPS. It reduces or eliminates signal degradation, resulting in improved accuracy.
- The system provides sub one-meter accuracy for accurate blast hole tagging and logging.
ViewShot 3DBlast Design Software
ViewShot 3D is a blast software that facilitates the planning, design and simulation of the blast outcome. Using DGPS in “plan mode”, the GPS coordinates from the drill rigs are imported into ViewShot 3D.
The blast design timing sequence is simulated and optimized using the timing design tools to achieve the desired outcomes. The blast plan and timing sequence is then downloaded onto the DGPS Tagger, ready for Tagging.
ViewShot Overview
DGPS Development
Future Applications
Future applications using DGPS include, a standalone module enabling DGPS capability on other equipment, MPU’s, drill rigs etc.; a common detonator list updated in real-time as multiple users or machines tag detonators; and centralized user interface – real time graphical update on deployment process.

